Homophone Identification and Merging for Code-switched Speech Recognition
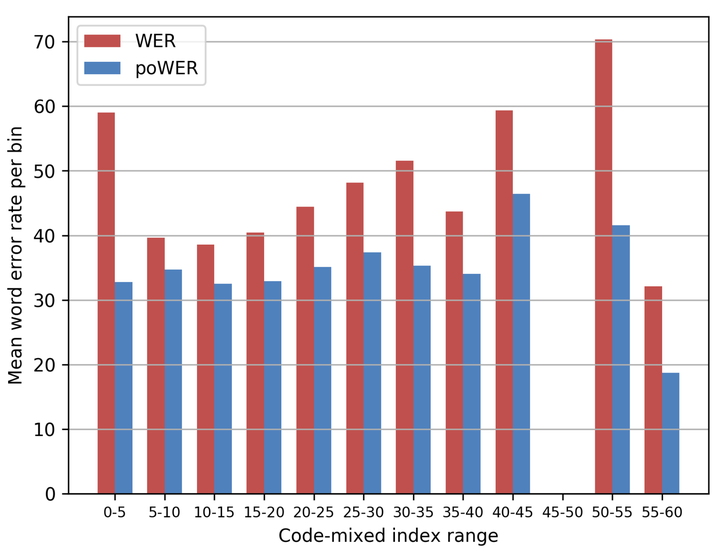 Pronunciation-Optimized Word Error Rate as compared to traditional WER vs Code-mixing index
Pronunciation-Optimized Word Error Rate as compared to traditional WER vs Code-mixing index
Abstract
Code-switching or mixing is the use of multiple languages in a single utterance or conversation. Borrowing occurs when a word from a foreign language becomes part of the vocabulary of a language. In multilingual societies, switching/mixing and borrowing are not always clearly distinguishable. Due to this, transcription of code-switched and borrowed words is often not standardized, and leads to the presence of homophones in the training data. In this work, we automatically identify and disambiguate homophones in code-switched data to improve recognition of code-switched speech. We use a WX-based common pronunciation scheme for both languages being mixed and unify the homophones during training, which results in a lower word error rate for systems built using this data. We also extend this framework to propose a metric for code-switched speech recognition that takes into account homophones in both languages while calculating WER, which can help provide a more accurate picture of errors the ASR system makes on code-switched speech.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code and math.